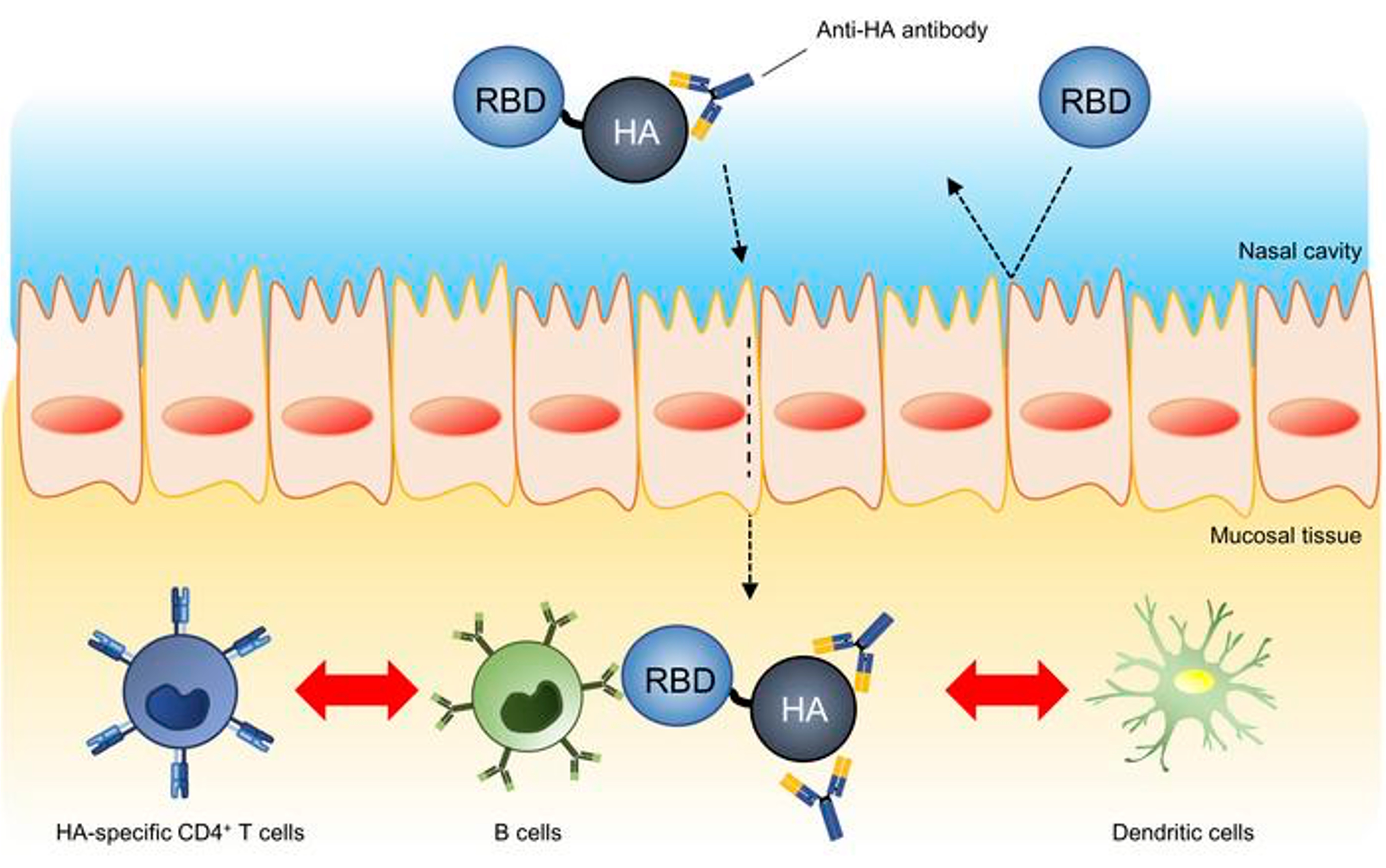
Intranasal immunization with an RBD-hemagglutinin fusion protein harnesses preexisting immunity to enhance antigen-specific responses (Yoshioka Lab, in JCI)
Intranasal vaccines are anticipated to be powerful tools for combating many infectious diseases, including SARS-CoV-2, because they induce not only systemic immunity but also mucosal immunity at the site of initial infection. However, they are generally inefficient in inducing an antigen-specific immune response without adjuvants. Here, we developed an adjuvant-free intranasal vaccine platform that utilizes the preexisting immunity induced by previous infection or vaccination to enhance vaccine effectiveness. We made RBD-HA, a fusion of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of spike derived from SARS-CoV-2 as a vaccine target with HA derived from influenza A virus (IAV) as a carrier protein. Intranasal immunization of previously IAV-infected mice with RBD-HA without an adjuvant elicited robust production of RBD-specific systemic IgG and mucosal IgA by utilizing both HA-specific preexisting IgG and CD4+ T cells. Consequently, the mice were efficiently protected from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Additionally, we demonstrated the high versatility of this intranasal vaccine platform by assessing various vaccine antigens and preexisting immunity associated with a variety of infectious diseases. The results of this study suggest the promising potential of this intranasal vaccine platform to address problems associated with intranasal vaccines.
This article was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, on Dec 12, 2023.
Title: “Intranasal immunization with an RBD-hemagglutinin fusion protein harnesses preexisting immunity to enhance antigen-specific responses”
Authors: Atsushi Kawai, Nagisa Tokunoh, Eigo Kawahara, Shigeyuki Tamiya, Shinya Okamura, Chikako Ono, Jessica Anindita, Hiroki Tanaka, Hidetaka Akita, Sho Yamasaki, Jun Kunisawa, Toru Okamoto, Yoshiharu Matsuura, Toshiro Hirai, Yasuo Yoshioka
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Intranasal immunization with an RBD-hemagglutinin fusion protein harnesses preexisting immunity to enhance antigen-specific responses (Yoshioka Lab, in JCI)