Aging impairs the ability of vascular endothelial stem cells to generate endothelial cells in mice (Takakura Lab, in Angiogenesis)
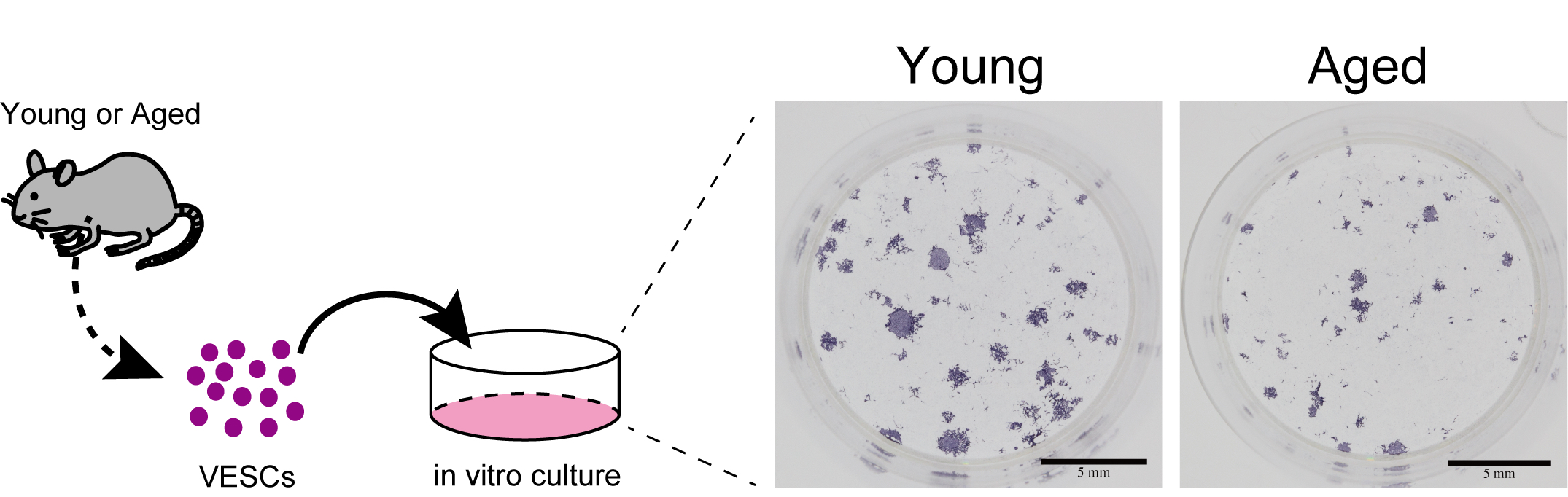
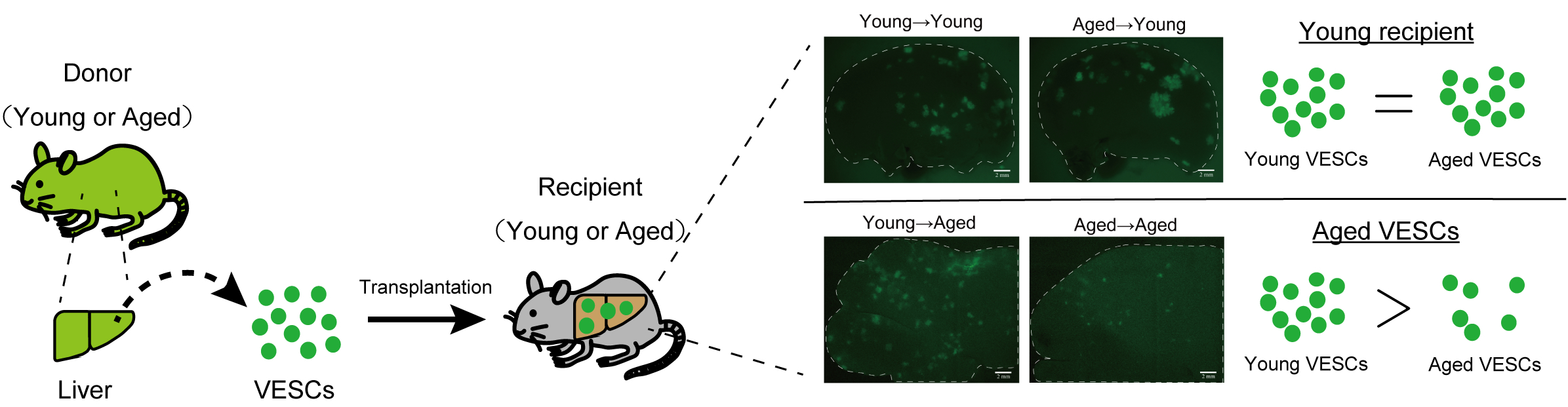
Tissue-resident vascular endothelial stem cells (VESCs), marked by expression of CD157, possess long-term repopulating potential and contribute to vascular regeneration and homeostasis in mice. Stem cell exhaustion is regarded as one of the hallmarks of aging and is being extensively studied in several types of tissue-resident stem cells; however, how aging affects VESCs has not been clarified yet. In the present study, we isolated VESCs from young and aged mice to compare their potential to differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we report that the number of liver endothelial cells (ECs) including VESCs was lower in aged (27-28 month-old) than young (2-3 month-old) mice. In vitro culture of primary VESCs revealed that the potential to generate ECs is impaired in aged VESCs isolated from liver and lung relative to young VESCs. Orthotopic transplantation of VESCs showed that aged VESCs and their progeny expand less efficiently than their young counterparts when transplanted into aged mice, but they are equally functional in young recipients. Gene expression analysis indicated that inflammatory signaling was more activated in aged ECs including VESCs. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from the Tabula Muris Consortium, we show that T cells and monocyte/macrophage lineage cells including Kupffer cells are enriched in the aged liver. These immune cells produce IL-1β and several chemokines, suggesting the possible involvement of age-associated inflammation in the functional decline of VESCs with age.
This article was published in Angiogenesis on August 10, 2023.
Title: “Aging impairs the ability of vascular endothelial stem cells to generate endothelial cells in mice”
Authors: Shota Shimizu, Tomohiro Iba, Hisamichi Naito, Fitriana Nur Rahmawati, Hirotaka Konishi, Weizhen Jia, Fumitaka Muramatsu and Nobuyuki Takakura
Links
-
Fig.1 Colony assays of vascular endothelial stem cells (VESCs). VESCs were isolated from mice (liver or lung) and cultured in vitro for 10 days. Then cells were fixed and underwent immunostaining with anti-CD31 antibody. Aged VESCs produced less ECs than young counterparts.
-
Fig.2 Transplantation of VESCs into vascular injury models. VESCs were isolated from EGFP mice (donor) and transplanted into vascular injured mice (recipient). In case of aged recipients, VESCs derived from young donors formed vessels more abundantly than aged VESCs (lower images). But young and aged VESCs were equally functional when transplanted into young recipients (upper images).
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Aging impairs the ability of vascular endothelial stem cells to generate endothelial cells in mice (Takakura Lab, in Angiogenesis)