Identification of multiple male reproductive tract-specific proteins that regulate sperm migration through the oviduct in mice (Ikawa Lab in PNAS)
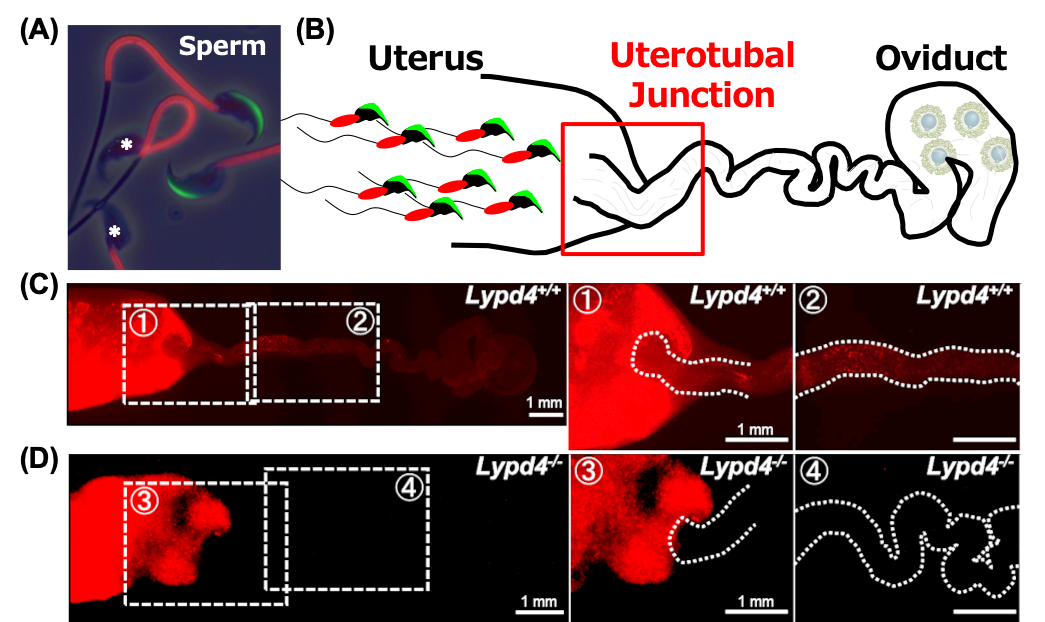
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing technology enables re- searchers to efficiently generate and analyze genetically modified animals. We have taken advantage of this game-changing tech- nology to uncover essential factors for fertility. In this study, we generated knockouts (KOs) of multiple male reproductive organ- specific genes and performed phenotypic screening of these null mutant mice to attempt to identify proteins essential for male fertility. We focused on making large deletions (dels) within 2 gene clusters encoding cystatin (CST) and prostate and testis expressed (PATE) proteins and individual gene mutations in 2 other gene families encoding glycerophosphodiester phosphodi- esterase domain (GDPD) containing and lymphocyte antigen 6 (Ly6)/Plaur domain (LYPD) containing proteins. These gene fami- lies were chosen because many of the genes demonstrate male reproductive tract-specific expression. Although Gdpd1 and Gdpd4 mutant mice were fertile, disruptions of Cst and Pate gene clusters and Lypd4 resulted in male sterility or severe fertility defects sec- ondary to impaired sperm migration through the oviduct. While absence of the epididymal protein families CST and PATE affect the localization of the sperm membrane protein A disintegrin and metallopeptidase domain 3 (ADAM3), the sperm acrosomal mem- brane protein LYPD4 regulates sperm fertilizing ability via an ADAM3-independent pathway. Thus, use of CRISPR/Cas9 technol- ogies has allowed us to quickly rule in and rule out proteins required for male fertility and expand our list of male-specific proteins that function in sperm migration through the oviduct.
This article will be published in Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (PNAS), on the week of Aug 26, 2019.
Title:“Identification of multiple male reproductive tract-specific proteins that regulate sperm migration through the oviduct in mice”
Authors:Fujihara Y, Noda T, Kobayashi K, Oji A, Kobayashi S, Matsumura T, Larasati T, Oura S, Kojima-Kita K, Yu Z, Matzuk MM, and Ikawa M.
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Identification of multiple male reproductive tract-specific proteins that regulate sperm migration through the oviduct in mice (Ikawa Lab in PNAS)