Identification of an endogenous antigen for MAIT cells (Yamasaki Lab, Sci. Immun.)
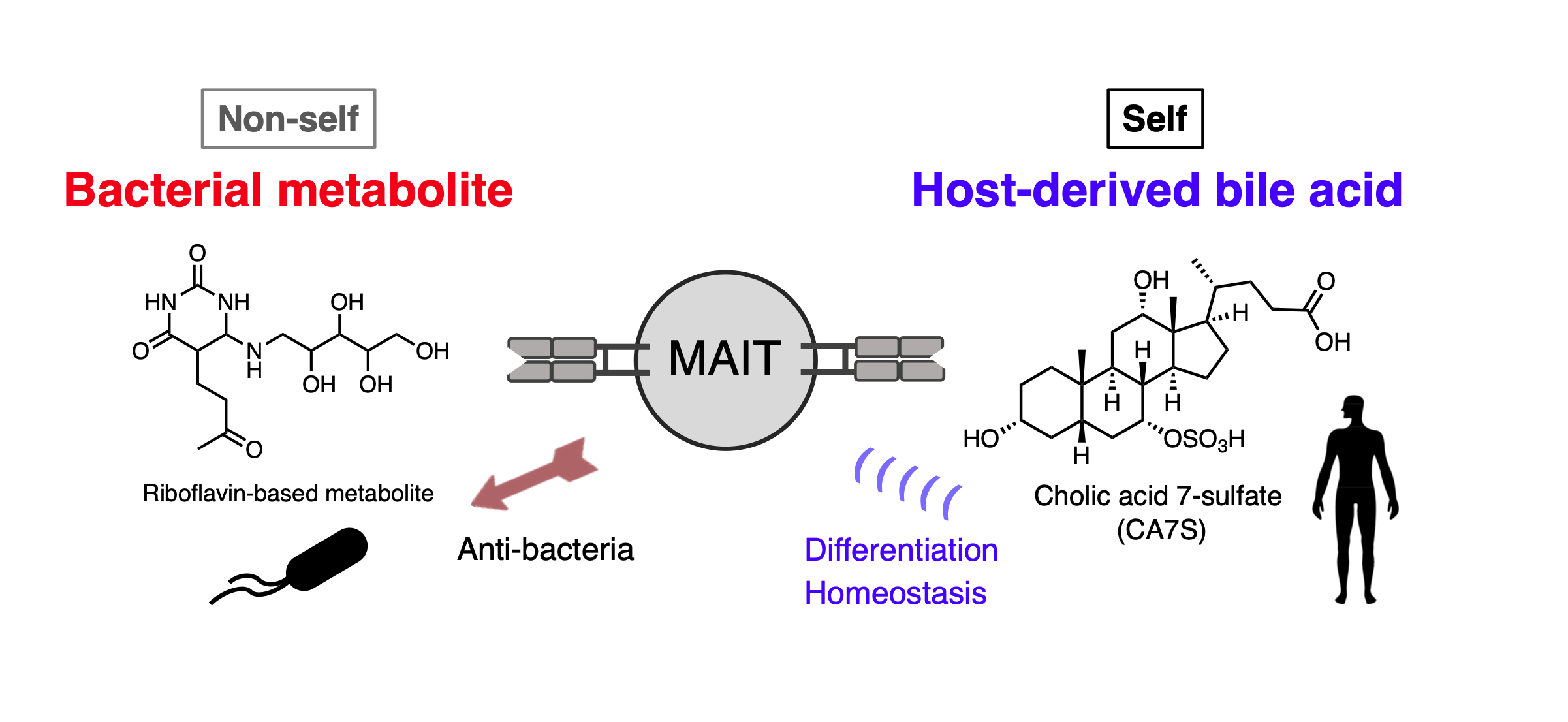
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are innate-like T cells that recognize bacterial riboflavin–based metabolites as activating antigens. Although MAIT cells are found in tissues, it is unknown whether any host tissue–derived antigens exist. Here, we report that a sulfated bile acid, cholic acid 7-sulfate (CA7S), binds the nonclassical MHC class I protein MR1 and is recognized by MAIT cells. CA7S is a host-derived metabolite whose levels were reduced by more than 98% in germ-free mice. Deletion of the sulfotransferase 2a family of enzymes (Sult2a1-8) responsible for CA7S synthesis reduced the number of thymic MAIT cells in mice. Moreover, recognition of CA7S induced MAIT cell survival and the expression of a homeostatic gene signature. By contrast, recognition of a previously described foreign antigen, 5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-d-ribitylaminouracil (5-OP-RU), drove MAIT cell proliferation and the expression of inflammatory genes. Thus, CA7S is an endogenous antigen for MAIT cells, which promotes their development and function.
This article was published in Science Immunology on January 26, 2024.
Title: “Sulfated bile acid is a host-derived ligand for MAIT cells”
Authors: Emi Ito, Shinsuke Inuki, Yoshihiro Izumi, Masatomo Takahashi, Yuki Dambayashi, Lisa Ciacchi, Wael Awad, Ami Takeyama, Kensuke Shibata, Shotaro Mori, Jeffrey Y. W. Mak, David P. Fairlie, Takeshi Bamba, Eri Ishikawa, Masamichi Nagae, Jamie Rossjohn and Sho Yamasaki* (*Corresponding Author)
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Identification of an endogenous antigen for MAIT cells (Yamasaki Lab, Sci. Immun.)