IFN-γ-induced Th1-Treg polarization in inflamed brains limits exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (Yamamoto Lab, in PNAS)
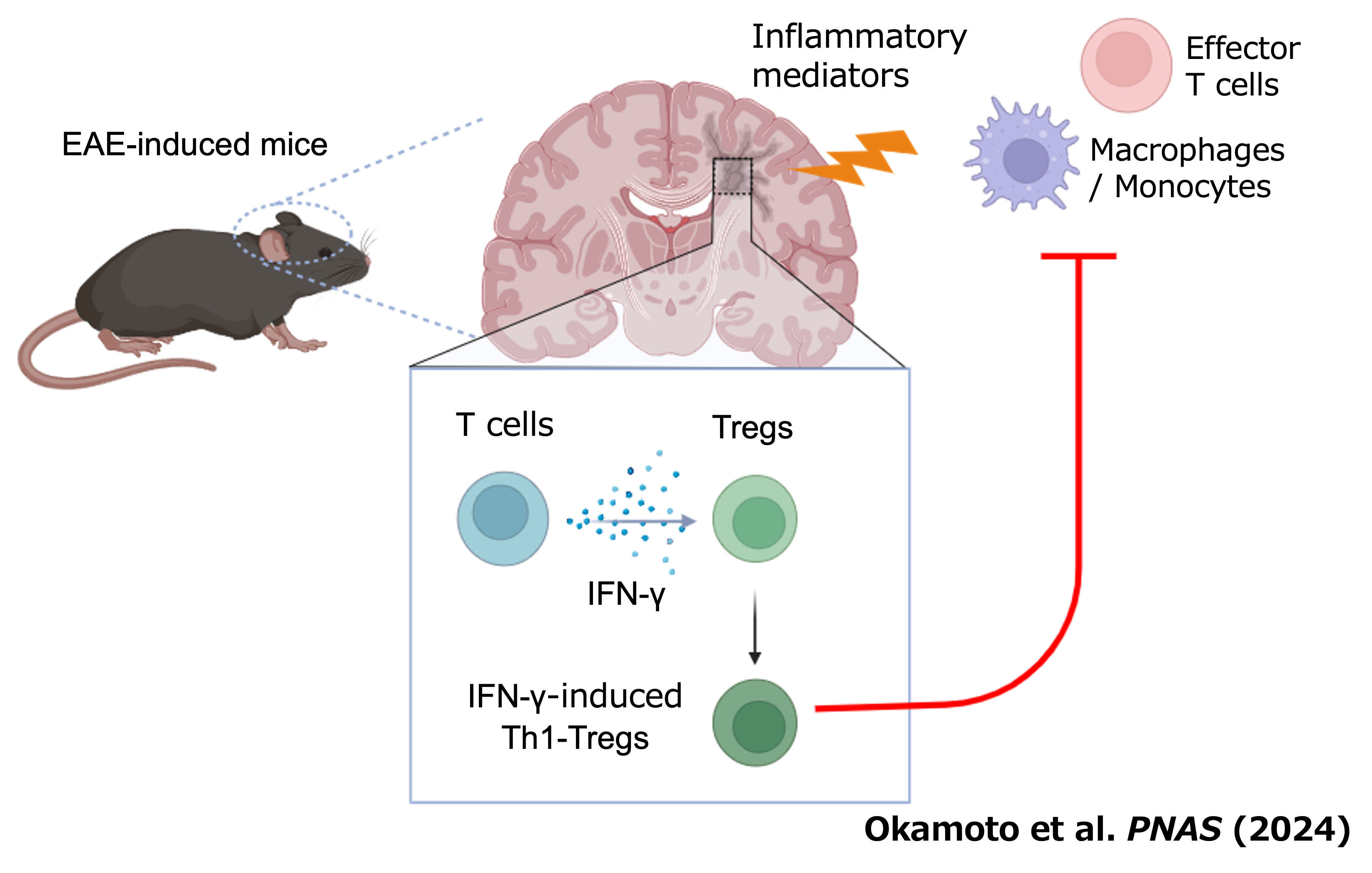
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is the most widely used rodent model for multiple sclerosis. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are individually well known to play beneficial roles in amelioration of EAE. However, little is known about the relationship between IFN-γ and Tregs during the disease. Here we show that IFN-γ polarizes Tregs into Th1-type Tregs (Th1-Tregs) to recover from EAE. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis revealed that brain Tregs showed signs of IFN-γ stimulation during EAE. Loss of IFN-γ signaling in Tregs and of T cell-derived IFN-γ impaired the Th1-Treg polarization and worsened the disease. Moreover, selective ablation of Th1-Tregs using an intersectional genetic method promoted pro-inflammatory features of macrophages in the inflamed brains and exacerbated the EAE. Taken together, our study highlights a critical role of T cell-derived IFN-γ for Th1-Treg polarization in inflamed brain to ameliorate EAE.
This article was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on Nov 2024.
Title: “IFN-γ-induced Th1-Treg polarization in inflamed brains limits exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis”
Authors: Masaaki Okamoto, Ayumi Kuratani, Daisuke Okuzaki, Naganori Kamiyama, Takashi Kobayashi, Miwa Sasai and Masahiro Yamamoto
DOI: 10.1073/pnas. 2401692121
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- IFN-γ-induced Th1-Treg polarization in inflamed brains limits exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (Yamamoto Lab, in PNAS)