Development of an mRNA-LNP Vaccine with Reduced Adverse Effects (Yoshioka Lab, in ACS Nano)
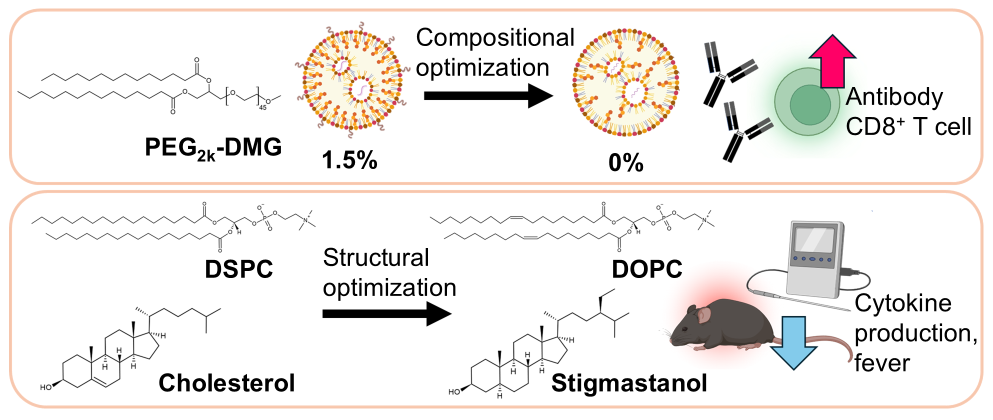
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines effectively induce antibody production and T cell responses. However, adverse reactions, such as fatigue and fever, following administration remain a key challenge. To modulate the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of mRNA vaccines, the optimization of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations has been attempted, particularly by screening ionizable lipids. In contrast, the potential impact of modifying other LNP components─poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-lipids, cholesterol, and phospholipids─on overall vaccine effects and adverse reactions remains underexplored. Here, we prepared mRNA-LNP formulations with altered structures and molar ratios of these components to assess their effects on in vivo protein expression, as well as on the induction of antigen-specific immune responses and adverse reactions. Reducing the PEG chain length and molar ratio of PEG-lipids increased antigen-specific antibody and CD8+ T cell responses. LNPs with cholesterol substituted by plant sterols, or LNPs with phospholipids replaced by those with different head and tail group structures, induced antigen-specific antibody and CD8+ T cell responses comparable to the control formulation. Alternately, these LNPs significantly reduced inflammatory cytokine production and adverse reactions, including fever, compared with the control LNPs. Finally, correlation analysis revealed a positive association between protein expression in specific organs and the magnitude of immune responses and adverse reactions. These findings demonstrate that modifying PEG-lipids, cholesterol, and phospholipids is beneficial for modulating the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of the mRNA-LNP vaccine.
This article was published in ACS Nano on July 23, 2025.
Journal : ACS Nano
Title : Modulating Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity in mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccines through Lipid Component Optimization
Authors : Yoshino Kawaguchi, Mari Kimura, Tatsuya Karaki, Hiroki Tanaka, Chikako Ono, Tatsuhiro Ishida, Yoshiharu Matsuura, Toshiro Hirai, Hidetaka Akita, Taro Shimizu, Yasuo Yoshioka
DOI : 10.1021/acsnano.5c10648
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Development of an mRNA-LNP Vaccine with Reduced Adverse Effects (Yoshioka Lab, in ACS Nano)