Cell Rep. 13(2):223-33 2015/10/13
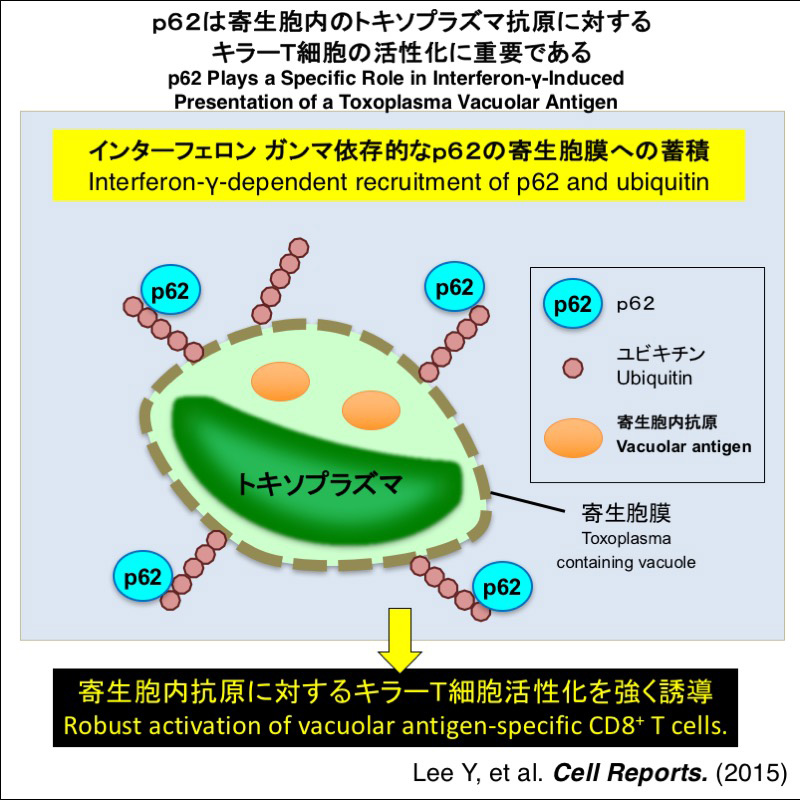
p62/Sqstm1 is a selective autophagy adaptor possessing ubiquitin binding domain. However, the role of p62 in host defense against Toxoplasma gondii infection is unclear. Here we show that IFN-γ stimulates ubiquitin and p62 recruitment to T. gondii parasitophorous vacuoles (PVs). Some essential autophagy-related proteins, but not all, are required for the ubiquitin and p62 recruitment to the PVs. Regardless of normal IFN-γ-induced T. gondii clearance activity and ubiquitination, the p62-deficiency in antigen presenting cells (APCs) and mice diminish IFN-γ-primed robust activation of CD8+ T cells that recognize the T. gondii-derived antigen secreted into PVs. Given that Atg3 and Irgm1/m3 expressions in APCs are essential for the PV disruption as well as ubiquitin and p62 recruitment and the vacuolar antigen-specific CD8+ T cell activation, IFN-γ-mediated ubiquitination and the following p62 recruitment to T. gondii are specifically required for the acquired immune response after the PV disruption by IFN-γ-inducible GTPases.
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Cell Rep. 13(2):223-33 2015/10/13