Nat Commun. 6:7035 2015/04/29
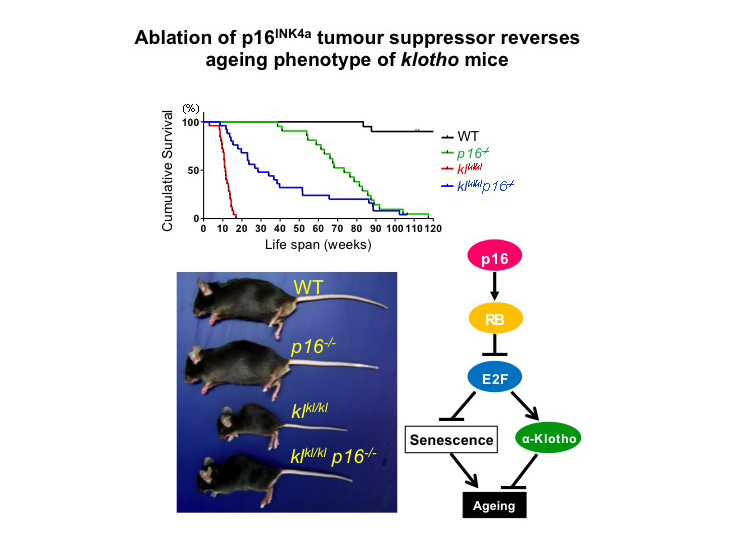
The p16INK4a tumour suppressor has an established role in the implementation of cellular senescence in stem/progenitor cells, which is thought to contribute to organismal ageing. However, since p16INK4a knockout mice die prematurely from cancer, whether p16INK4a truly reduces longevity remains unclear. Here we show that, in mutant mice homozygous for a hypomorphic allele of the α-klotho ageing-suppressor gene (klkl/kl), accelerated ageing phenotypes are rescued by p16INK4a ablation. Surprisingly, this is due to the restoration of α-klotho expression in klkl/kl mice and does not occur when p16INK4a is ablated in α-klotho knockout mice (kl-/-), suggesting that p16INK4a is an upstream regulator of α-klotho expression. Indeed, p16INK4a represses α-klotho promoter activity by blocking the functions of E2Fs. These results, together with the observation that the expression levels of p16INK4a are inversely correlated with those of α-klotho throughout ageing, indicate that p16INK4a plays a previously unrecognised role in down-regulating α-klotho expression during ageing. These results advance our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the development and progression of ageing in mammals.
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- Nat Commun. 6:7035 2015/04/29