PLoS Pathog 9:e1003150 2013/02/07
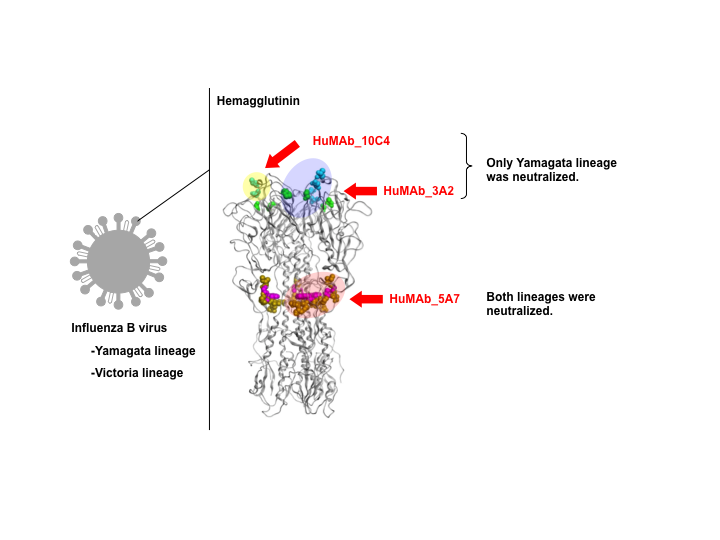
Influenza virus has the ability to evade host immune surveillance through rapid viral genetic drift and reassortment; therefore, it remains a continuous public health threat. Recently, developments of vaccines producing broadly reactive antibodies, as well as of therapeutic strategies using human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (HuMAbs) with global reactivity, have been gathering a great interest. The present study reports a HuMAb neutralizing a wide range of influenza B viruses. This HuMAb recognizes the conserved region of hemagglutinin. Moreover, therapeutic efficacy of this HuMAb was also confirmed by in vivo animal experiments. Thus, this study provides insight for the development of broad-spectrum therapeutics and a universal prophylactic vaccine against influenza B virus.
Links
- Home
- Achievement
- Research Activities
- PLoS Pathog 9:e1003150 2013/02/07