GPI (Glycosylphosphatidylinositol)-anchor is a glycolipid consisting of phosphatidylinositol (PI), glucosamine (GlcN), mannose (Man) and ethanolaminephosphate (EtNP), and acts as a lipid anchor for various plasma-membrane proteins. GPI-anchored proteins play important roles in hostŐs self-defense, intercellular signal transduction, and so on. Besides, some of them function as receptors for viruses and toxins. GPI-anchor is widely distributed and conserved in various eukaryotes and is essential for development in higher animals as well as for growth of yeasts and protozoan parasites.
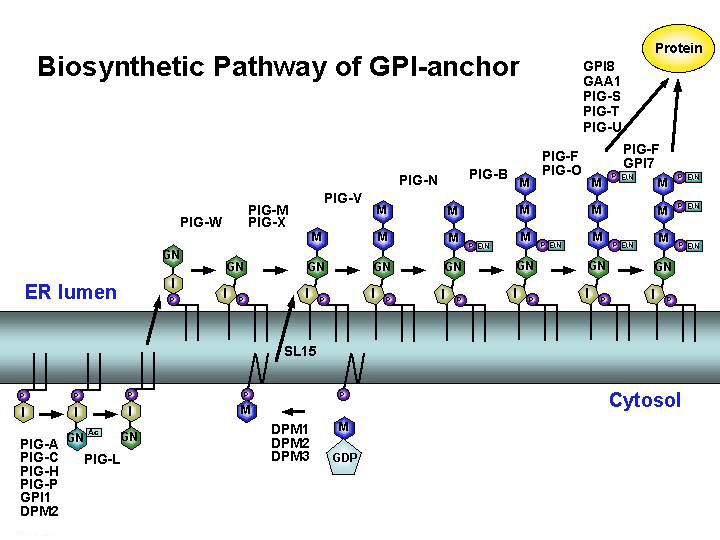
Our final goal is to identify all genes involved in the biosynthesis of GPI-anchor. GPI is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by sequential 10-step enzyme reactions. In 1992, we first cloned PIG-A, a catalytic component of the first step, using GPI-negative cell line. Since then, more than twenty PIG-genes involved in these reactions have been identified by our group.
The first step, the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to PI generating GlcNAc-PI, is catalyzed by an enzyme complex consisting of at least seven components, PIG-A, PIG-C, PIG-H, PIG-P, GPI1, DPM2 and PIG-Y. In the second step, GlcNAc moiety is de-N-acetylated by PIG-L. These two reactions occur on the cytoplasmic surface of the ER.
GPI intermediate is then flipped into the luminal side of the ER. There, Inositol moiety is acylatd by PIG-W generating GlcN-acyl-PI. Next, three Man and three EtNP are sequentially added to GlcN-acyl-PI. Three distinct mannosyltransferases, PIG-M, PIG-V and PIG-B, were identified, and PIG-M required the essential counterpart PIG-X. The donor substrate dolichol-phosphate-mannose is synthesized by the enzyme complex of DPM1, DPM2 and DPM3, and its translocation into the luminal side of the ER is mediated by SL15. The transfer of EtNP to the first, third and second Man are catalyzed by PIG-N, PIG-O and GPI7. PIG-F, an essential subcomponent, binds PIG-O and GPI7 independently.
The amido-group of EtNP added by PIG-O/PIG-F are finally transferred to the carboxyl terminus of proteins by GPI-transamidase generating GPI-anchored proteins. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme complex of the catalytic subunit GPI8 and the four essential subcomponents, GAA1, PIG-S, PIG-T and PIG-U. GPI-anchored proteins depart from the ER and are transported to the plasma membrane via Golgi apparatus.
Now, we are investigating on further identification of new genes, reconstitution of components, regulatory mechanism and so on.