We are investigating the molecular biological mechanisms involved in human diseases, especially cardiovascular diseases, by using animal models.
1) We have established a diastolic heart failure model using Dahl salt-sensitive rats. This model showed that left ventricular (LV) fibrosis and stiffening play crucial roles in the development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Digitalis-like factors and the subsequently activated Na+/Ca2+ exchanger entry mode may play important roles in the development of hypertensive HFpEF and the effect of carnitine when it is administered to the HFpEF model (3). In addition, serum interleukin-16 (IL-16) levels are elevated in patients with HFpEF and the rat model (1). Enhanced cardiac expression of IL-16 in transgenic mice induces cardiac fibrosis and LV myocardial stiffening that is accompanied by increased macrophage infiltration (Figure 1).
2) To understand the cellular and molecular aspects of vascular smooth muscle (SM) cell growth in atherosclerotic plaques, we characterized the transcriptional mechanisms of SM-specific genes, especially, the human SM alpha-actin (SmαA) gene (Figure 2). Several cis-acting DNA elements and transcriptional nuclear factors that are essential for SmαA expression have been identified. Since SmαA is also expressed in many tissues during acute inflammation, we are analyzing its gene expression and its functions.
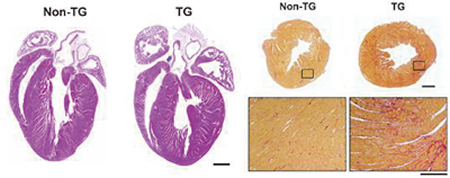
Figure 1. Enhanced cardiac expression of IL-16 under the α-MHC promoter causes increased myocardial fibrosis and stiffness in mice. (left) Four-chamber view of the hearts from non-transgenic and transgenic mice. (right) Sirius Red-stained heart LV sections of fibrosis areas.
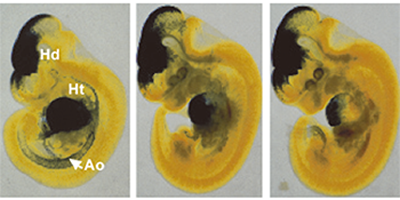
Figure 2. The human vascular smooth muscle α-actin promoter (left) expressed in embryonic aorta (Ao), but those including -1M (center) and 4M (right) point mutants in the transcriptional nuclear factor binding regions specifically did not.